From equality to global poverty: the Covid-19 effects on societies and economies
The Covid-19 pandemic is a social and an economic crisis just as much as it is a health one – its repercussions, severe and far-reaching, are being felt across the world.

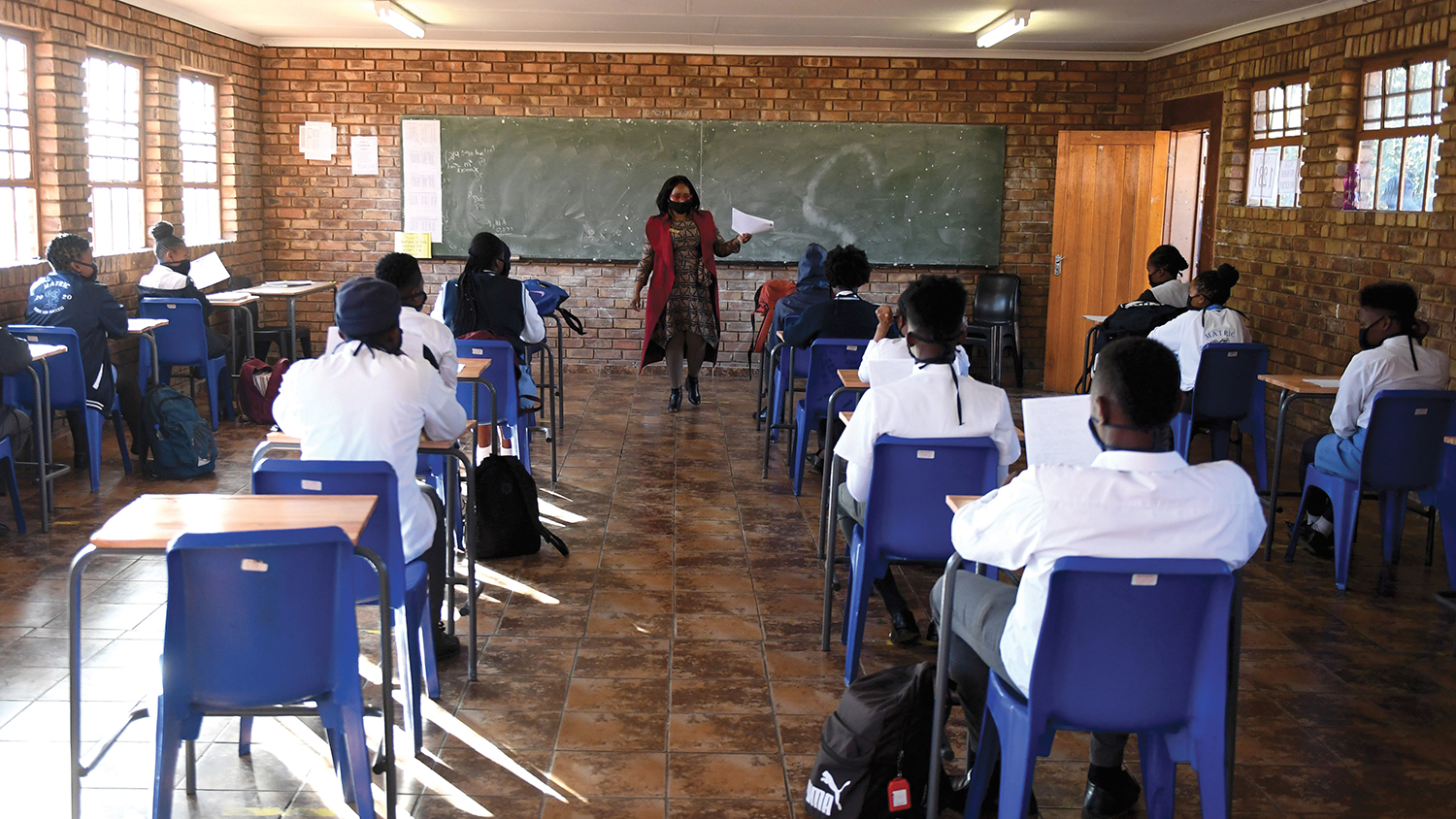
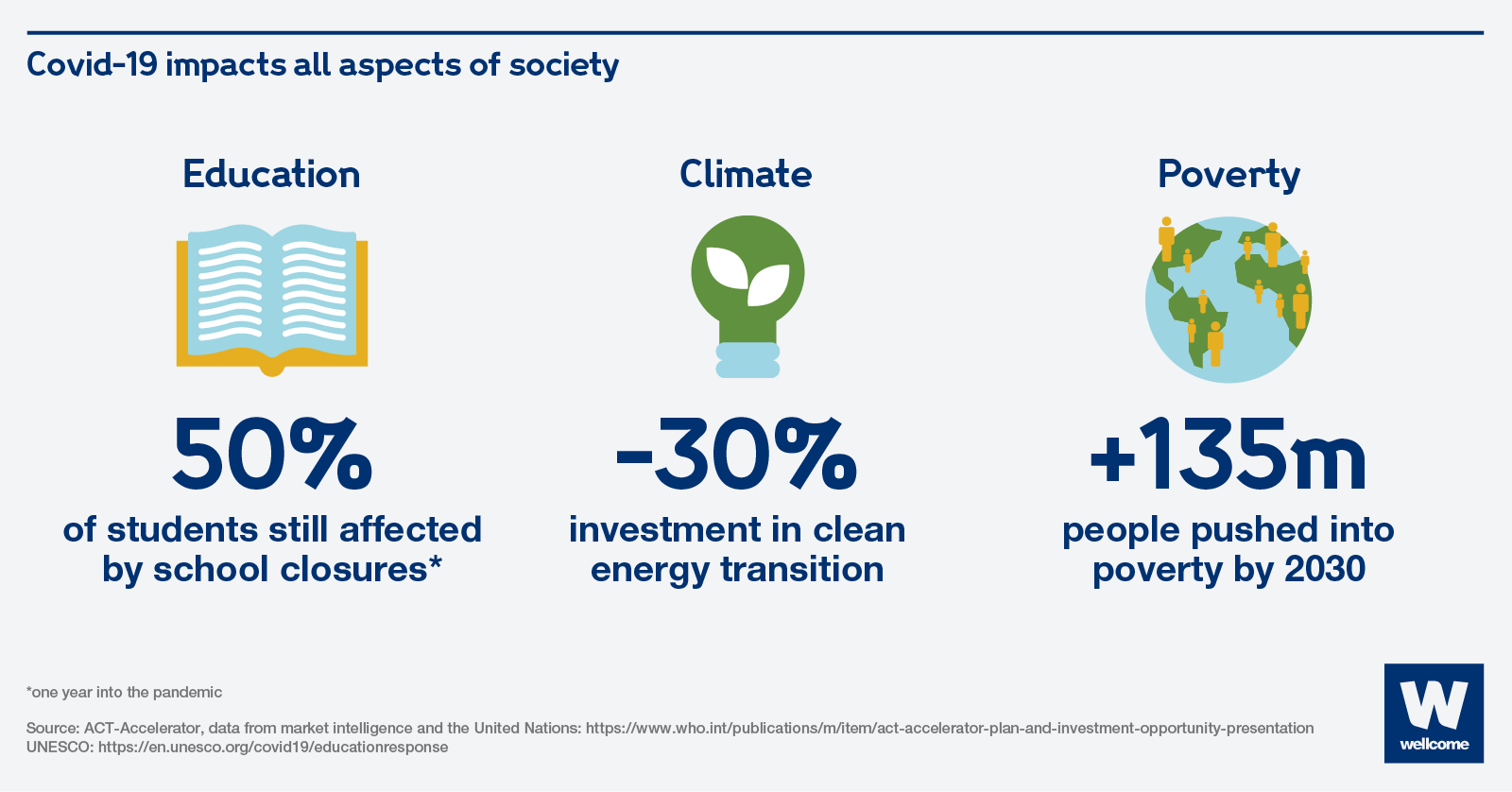
One year into the pandemic, almost half of the world’s students were affected by school closures. Millions of girls might not be going back at all.

From school closures to devasted industries and millions of jobs lost – the social and economic costs of the pandemic are many and varied. Covid-19 is threatening to widen inequalities everywhere, undermine progress on global poverty and clean energy, and more.
The best solution is to stop this damage from happening, through the use of tests, treatments and vaccines everywhere they're needed. This will cost only a fraction of the huge economic loss the pandemic is causing every week.
To slow the spread of the virus, schools closed across the world. One year into the pandemic, almost half of the world’s students are still affected by school closures. Millions of girls in some countries might not be going back at all, putting them at risk of adolescent pregnancy, child marriage and violence.

Source: ACT-Accelerator, data from market intelligence and the United Nations: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/act-accelerator-plan-and-investment-opportunity-presentation
UNESCO: https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse
Businesses closed too, leading to the equivalent of 255 million full-time jobs lost, in terms of working hours, in 2020. Among the worst hit are workers in the informal economy, young people and women. Any economic recovery will likely be uneven, leading to greater inequality in the coming years.
Women have been harder hit economically by the pandemic because they are a large proportion of the workers in sectors severely affected by Covid-19, including accommodation and food services, and in front-line occupations, such as the health and social care sectors.
With the closures of schools, they have also had to take on more care responsibilities at home. Whether through job losses or school closures, the pandemic threatens to undo decades of progress on gender equality.
Covid-19 has been slowing down progress on clean energy too, at least temporarily, by curbing investments and delaying the expansion of clean energy technologies.
There has been some positive climate news: global energy-related CO2 emissions fell by 5.8% in 2020, the largest ever decline in global CO2 emissions in history. But that’s only a short-term effect of lockdowns, not a sustained change. In fact, emissions are expected to rise by 4.8% in 2021, the second highest rate in history, as the demand for coal, oil and gas rebounds with the economy.
The pandemic will likely trigger the biggest recession since World War II, causing a financial loss twice as great as during the 2008 recession. That’s a staggering $12 trillion the global economy will lose over 2020 and 2021.

The effects are felt unevenly across societies.
While no economy is left untouched, lower- and middle-income countries are worst affected because they have weak defences against economic shocks and tend to depend more on a few sectors, such as commodities and tourism.
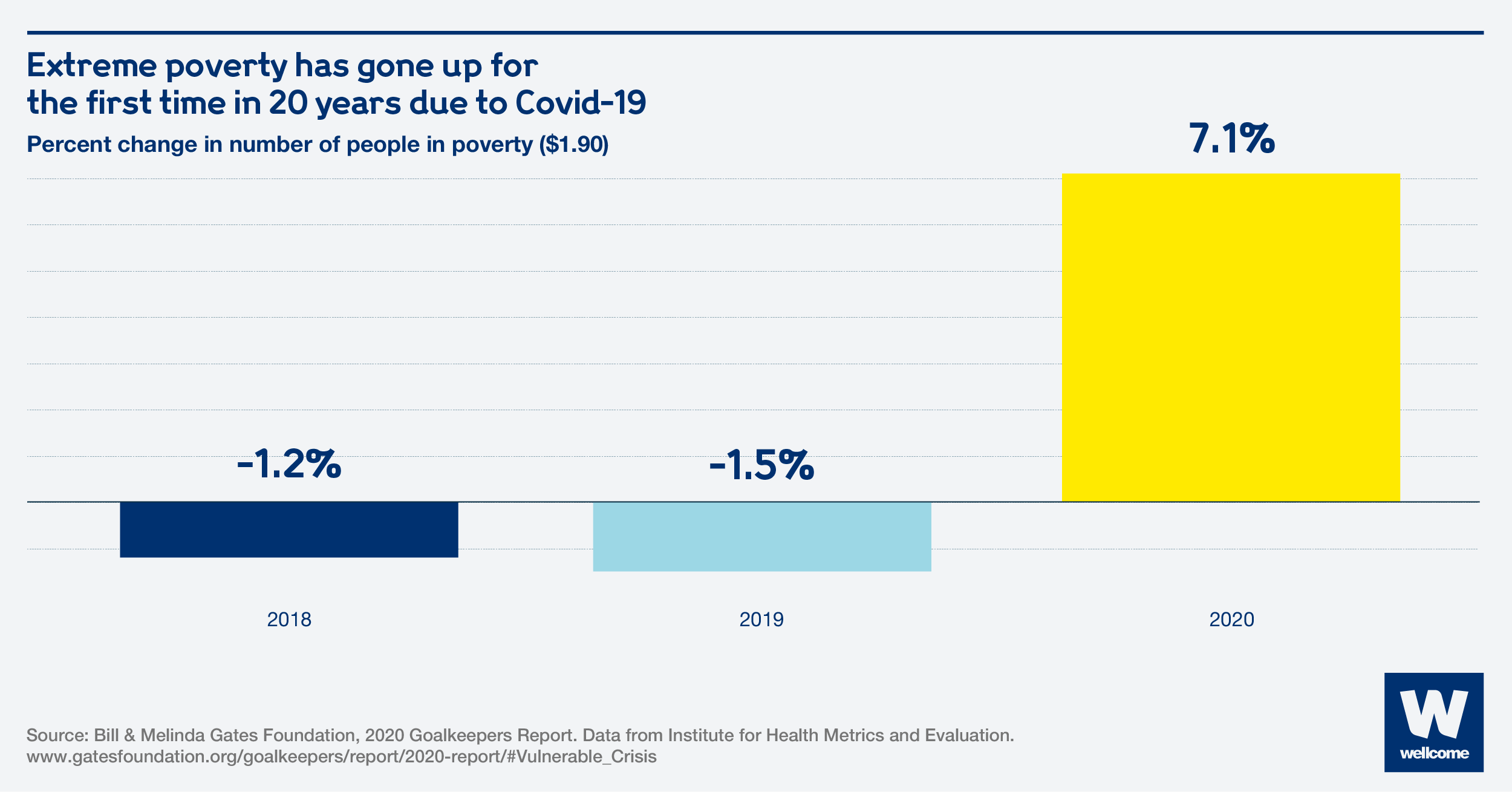
Millions of people have already fallen below the poverty line. In just a few months of Covid-19, extreme poverty went up for the first time in 20 years.
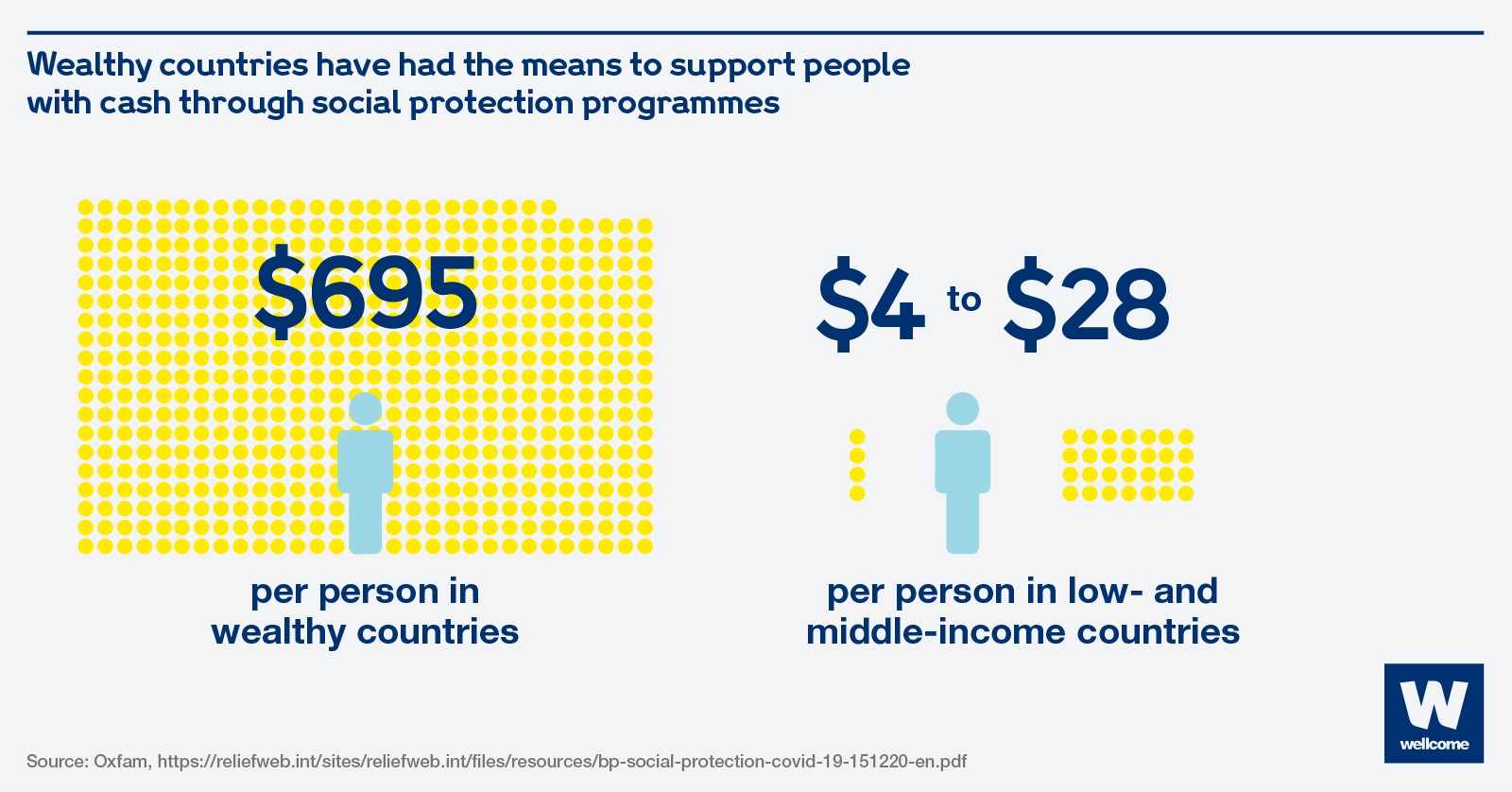
Wealthy countries have had the means to intervene early to protect people and businesses, by pumping $9.8 trillion into their economies, the biggest chunk of the total of $11.7 trillion spent globally, to cope with the fallout from the pandemic. But low- and middle-income countries have not been able to do the same.
A report by Oxfam reviewed the government measures to support people through the pandemic in 126 low- and middle-income countries, including numerous kinds of benefits for those affected, and found that 97% of the support provided was inadequate to meet basic needs.

Wealthy countries spent on average $695 per person, while low- and middle-income countries spent between $4 and $28 per person for cash support during 2020.
The Access to COVID-19 Tools (ACT) Accelerator is a global collaboration of health organisations, scientists, businesses, civil society, governments and philanthropies, including Wellcome, working together to get lifesaving tests, treatments and vaccines from the laboratory to the front line. An investment of $18.5 billion is still needed in 2021 to fund that work.
Without tangible solutions to stop the virus from spreading and treat those who fall ill, the pandemic will continue to steal lives and livelihoods.
The greatest investment we could make now is in the research, development and fair distribution of tests, vaccines and treatments.
The good news is that the investment needed – $18.5 billion this year, as estimated by the ACT-Accelerator – is small compared to what the world will keep losing if we don’t act. For every month’s delay in expanding access to Covid-19 vaccines, tests and treatments equitably around the world, the world is losing 120,000 lives and $460 billion in economic output, the International Monetary Fund estimates.
The investment needed relies on countries and international organisations showing leadership, pooling resources together and acknowledging that this crisis can only be overcome if we act together.
This article was first published in September 2020, and updated in May 2021.
Did you find this content useful? Let us know your feedback at webmaster@wellcome.org.






The Covid-19 pandemic is a social and an economic crisis just as much as it is a health one – its repercussions, severe and far-reaching, are being felt across the world.