The cost of not preparing for infectious diseases
Covid-19 will cost governments an estimated US$11 trillion by the end of 2021. In 2018, epidemics reportedly cost the world $60 billion a year.
Not preparing for infectious disease outbreaks costs far more than putting the systems in place to prevent them from spreading around the globe. Here’s why.

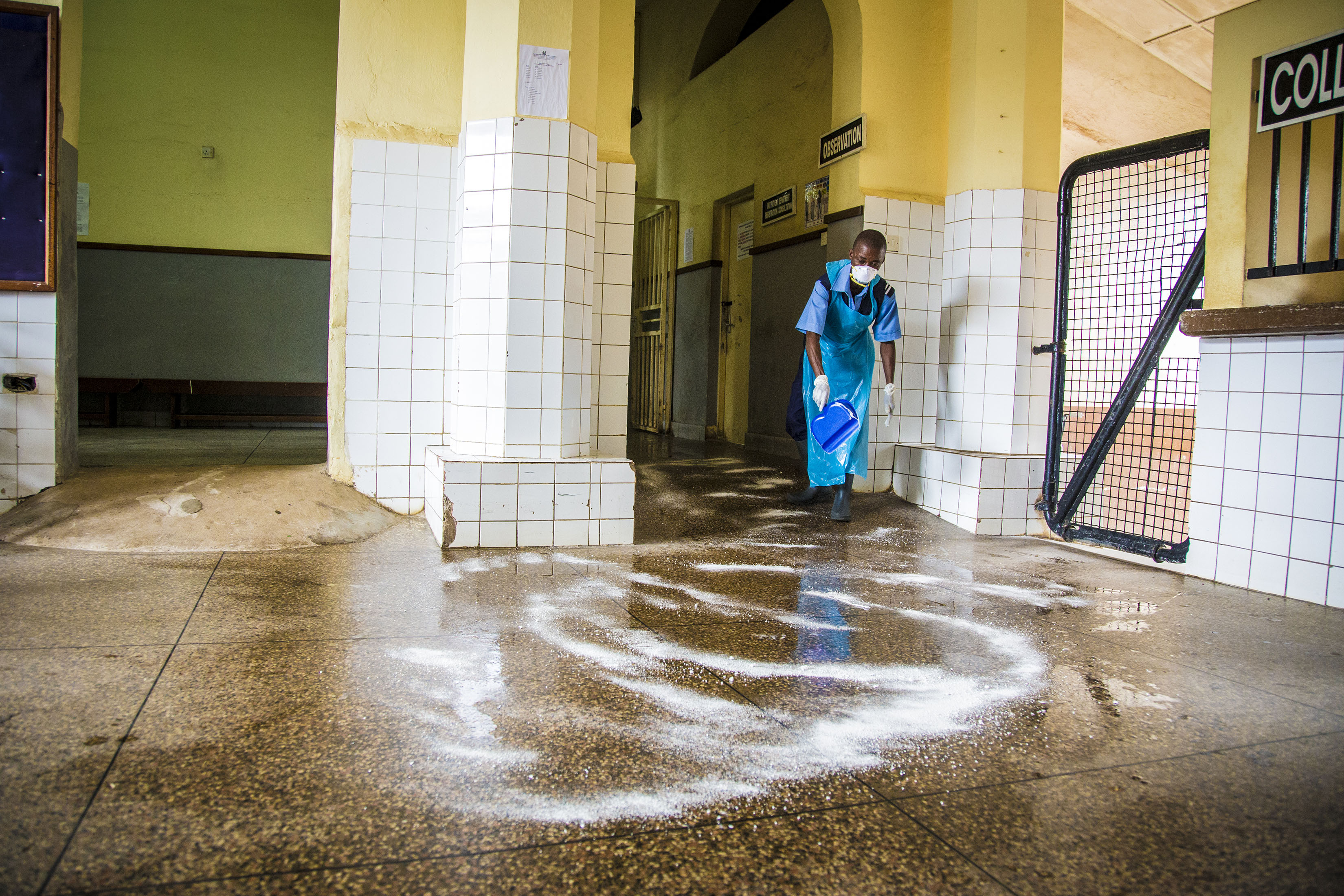
Freetown, Sierra Leone
During the Ebola crisis of 2014, Connaught Hospital was the main referral centre for Sierra Leone. There was an overwhelming surge in patients, and many staff were infected and even died. The hospital was almost forced to close, but thanks to the courage and commitment of numerous healthcare workers like this one, it stayed open. Chlorine powder was used to disinfect the emergency entrance, helping reduce the spread of infection within the hospital.
When we think about how hospitals save lives, we don’t always picture the cleaner. But without rigorous disinfection and sterilisation protocols, hospitals can put at risk the very lives they are trying to save. And during a major epidemic, the work of the cleaning staff becomes all the more vital in minimising rates of infection.

There are more epidemics than the general public hears about – most don’t make the headlines.
Take Ebola. Since it emerged in 1976, there have been 36 deadly outbreaks.
Source: CDC, 2021
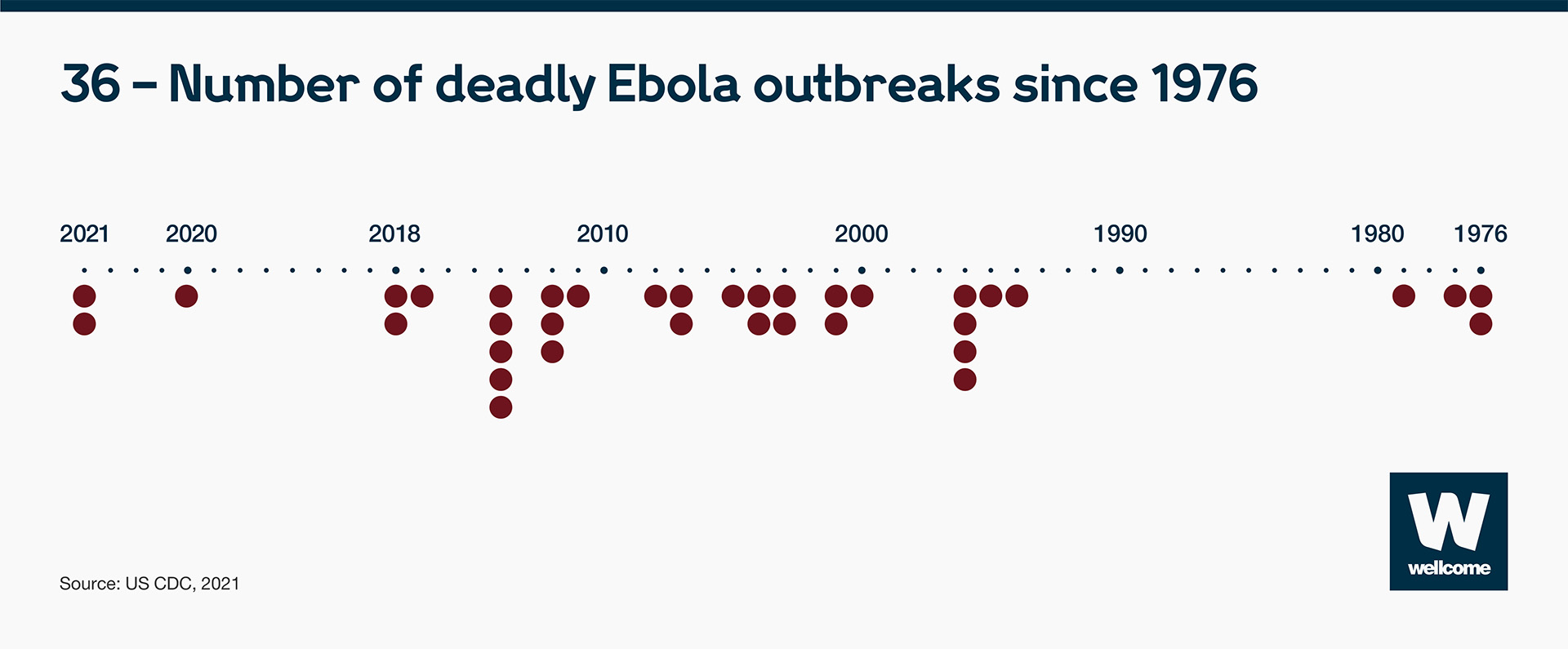
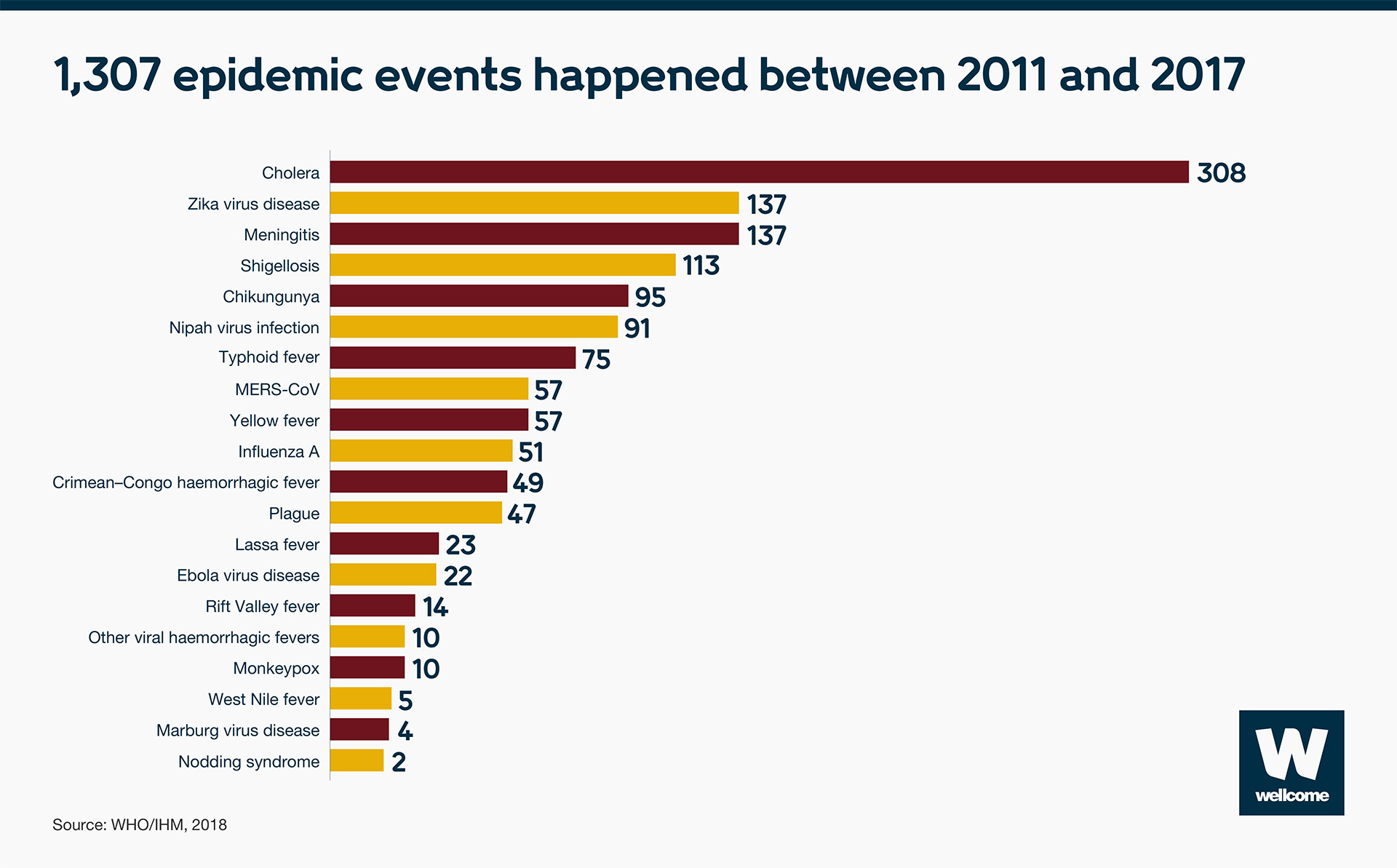
That represents just one infectious disease. In a six-year period (2011-2017) many more epidemics happened – the equivalent to over 186 every year.

Source: WHO/IHM, 2018
Pandemics and epidemics are costly to fight, and have a big impact on economies. Expenditures for prevention and preparedness are measured in billions of dollars, the cost of a pandemic in trillions. Currently, Covid-19 is estimated to cost the world $11 trillion. The World Health Organisation notes that it would take 500 years to spend as much on investing in preparedness as the world is losing due to Covid-19.
Pandemics can have a long-lasting impact on the global economy.
Due to the current Covid-19 pandemic, extreme poverty has increased for the first time in 20 years.

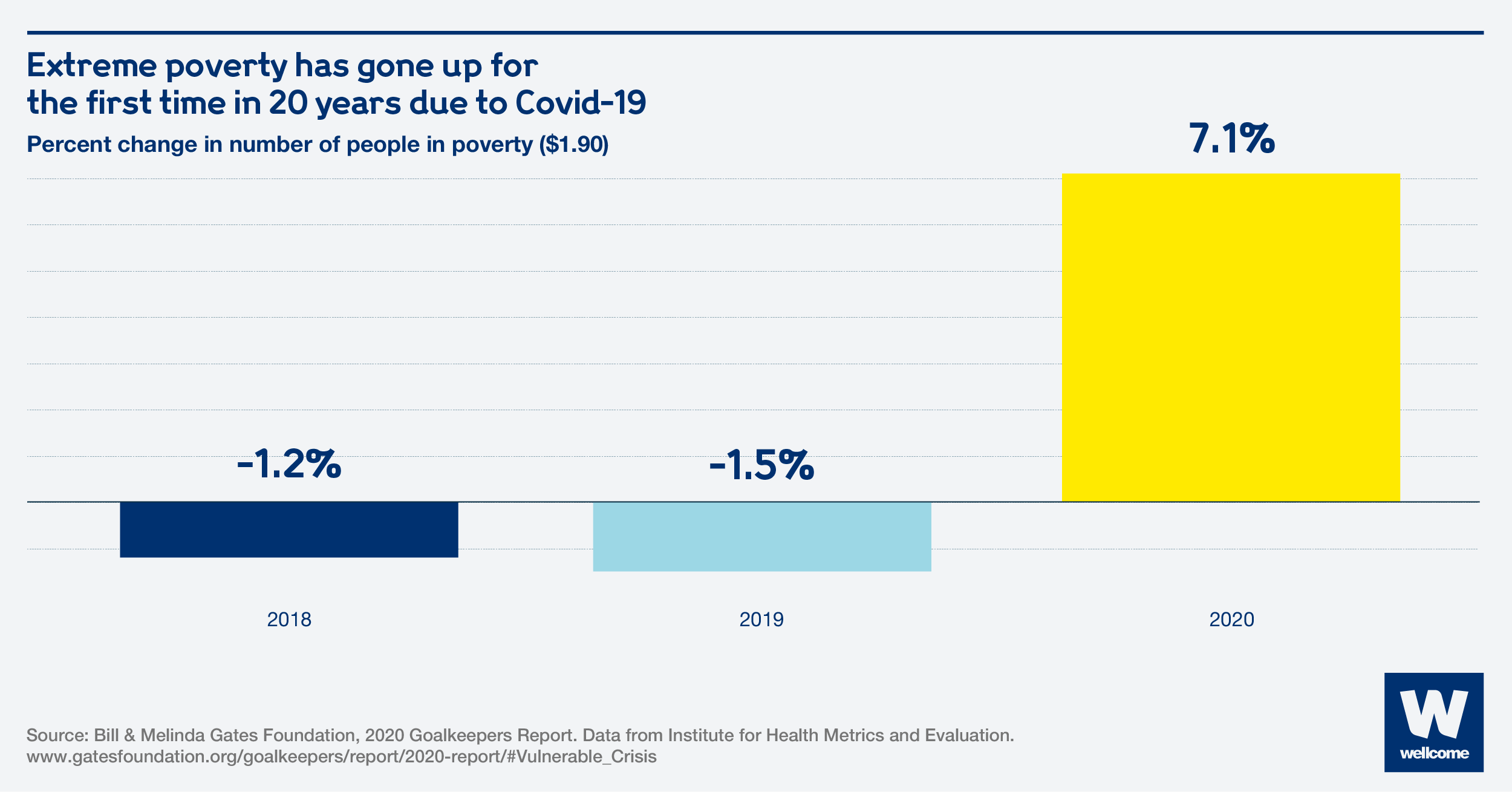
The cost of epidemics is unsustainable. They devastate the world’s poorest countries, lessening their ability to develop economically.

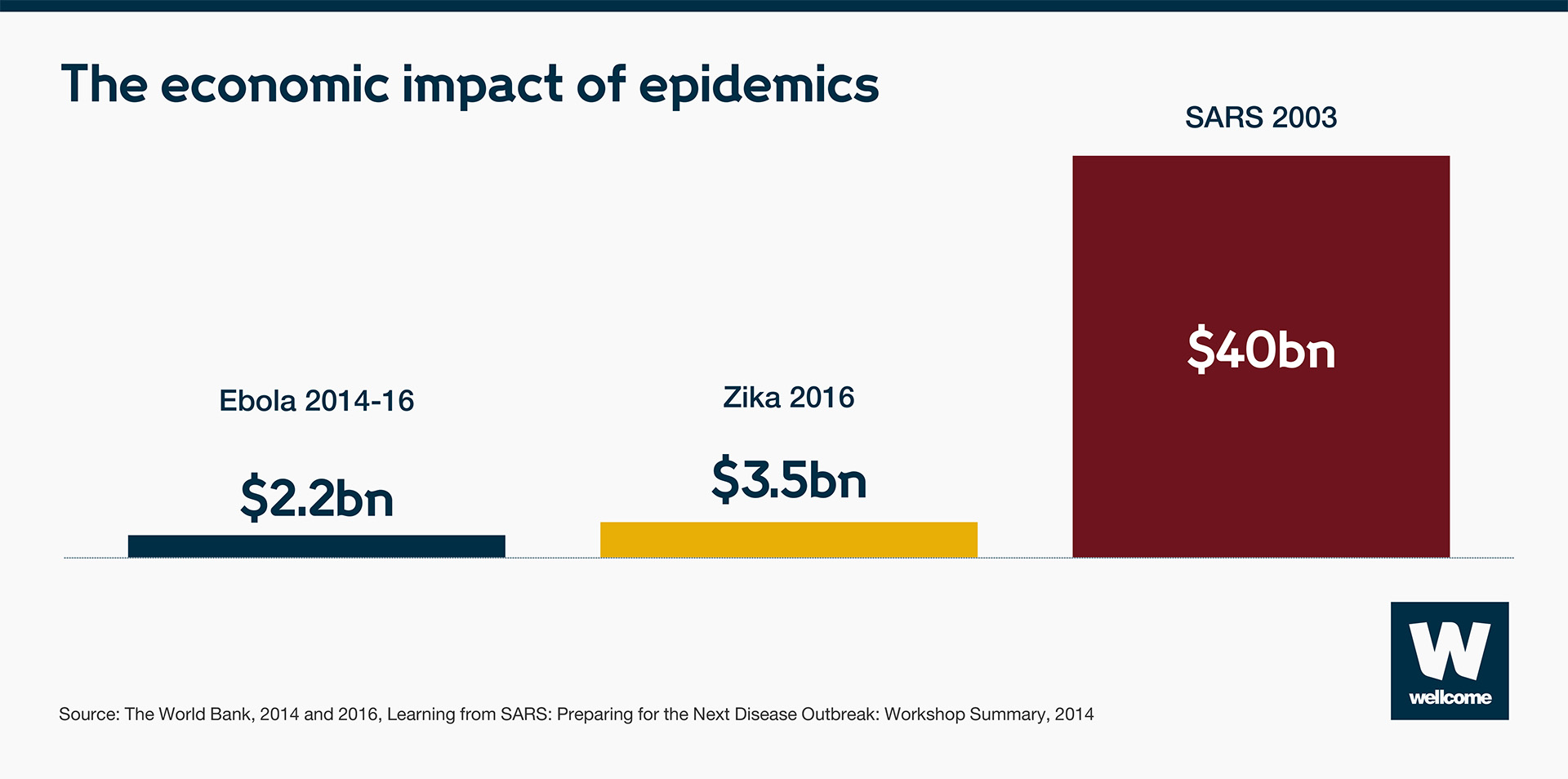
In 2014, when Ebola struck in West Africa, $2.2bn of economic growth was lost in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. When Zika hit the Americas in 2016, the short-term economic impact was $3.5bn. And when SARS spread through Asia in 2003, affected countries’ GDPs lost $40bn.
To take another example, MERS. When it infiltrated Seoul from Saudi Arabia in 2015, spread rapidly through South Korea in two months.

Source: WHO, 2016
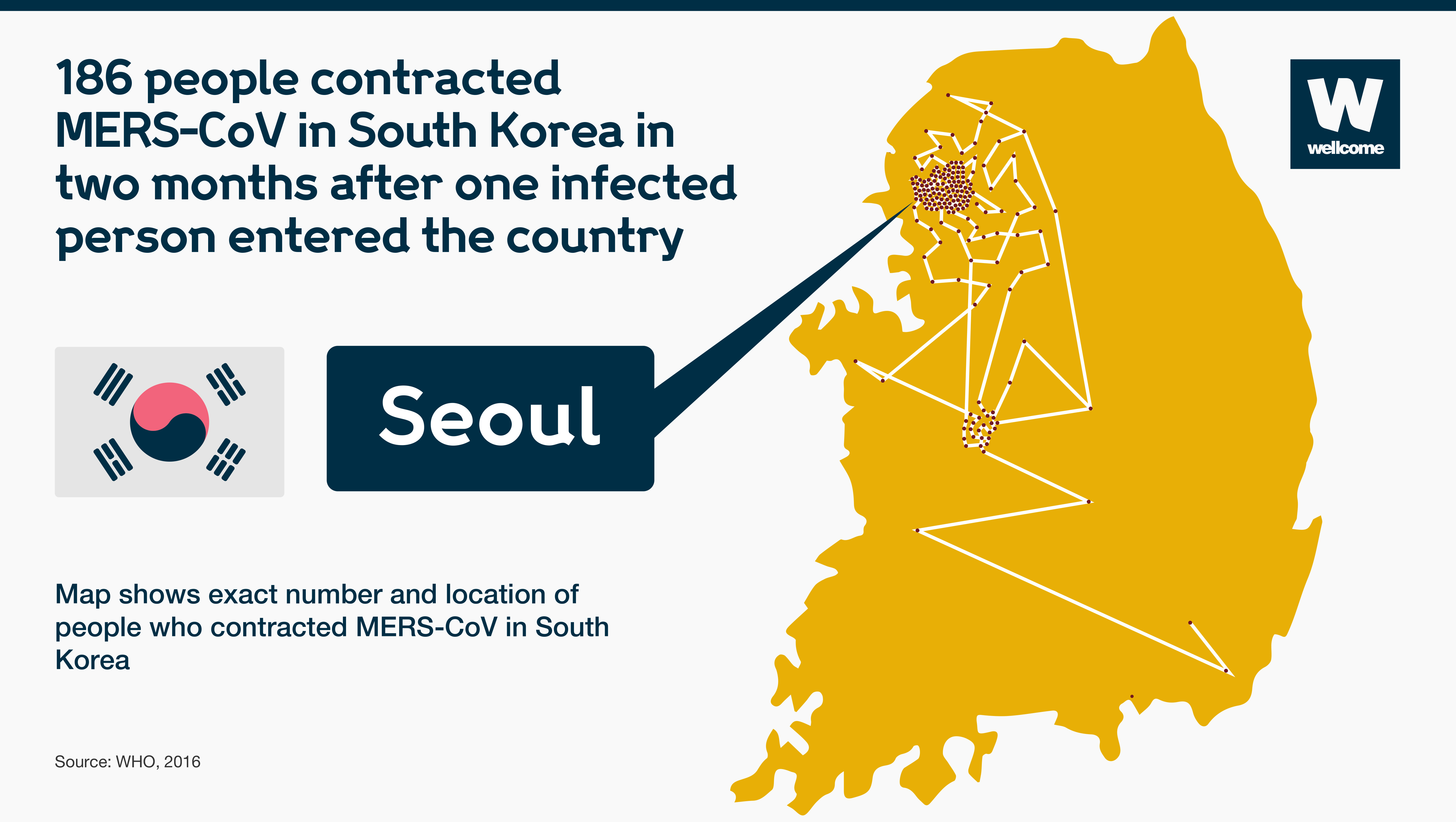
At $8bn, the expense of stamping out MERS over that period cost more than the country makes each year from exporting computers.
But the economic cost of fighting infectious disease must not obscure what lies squarely in its path: people.
Whole communities and regions were devastated by the West African Ebola outbreak, with the virus infecting 28,616 people. Nearly half of them died.

Source: CDC, 2021

The hardest hit were the most vulnerable people in society: children.

Source: CDC, 2016

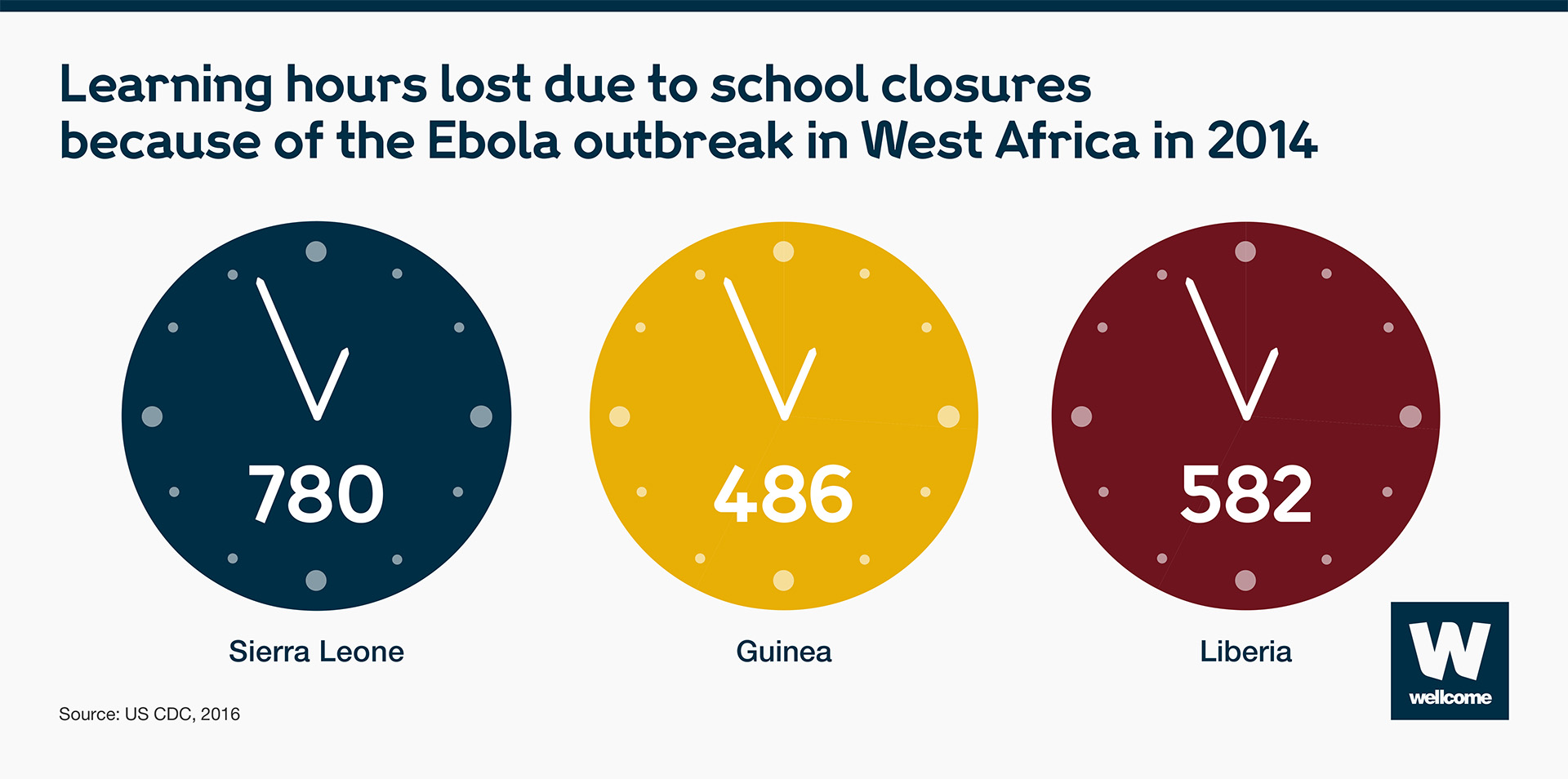
Aside from the impact on their emotional wellbeing, children face another challenge as a result of surviving an epidemic – the impact on their potential for future employment and earnings due to loss of education.

Learning hours lost due to Ebola in 2014: Sierra Leone - 780 hours, Guinea - 486 hours, Liberia - 582 hours.
Source: CDC, 2016
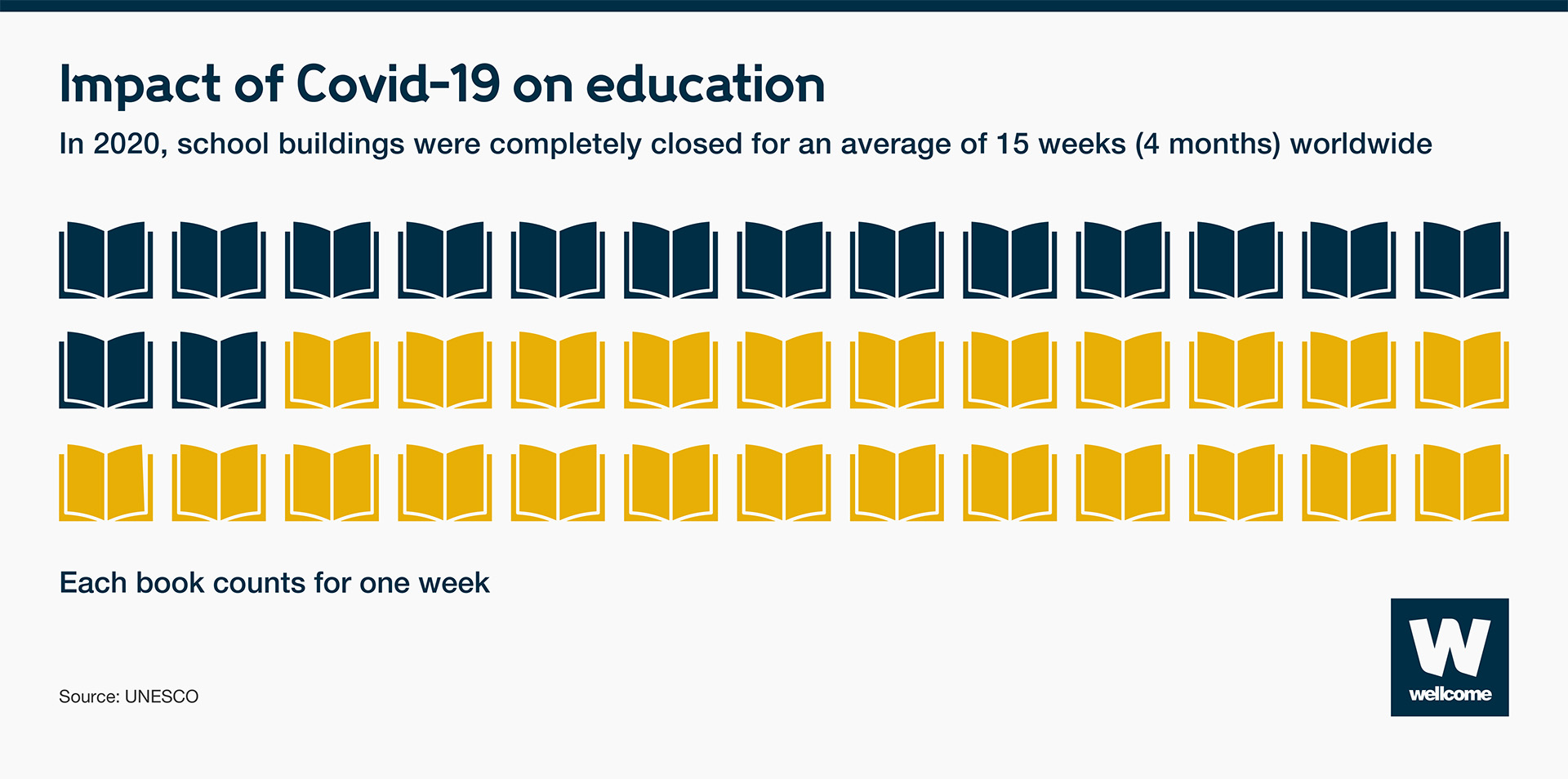
To slow the spread of Covid-19, schools closed across the world. As a result, it’s estimated that 100 million children will fall below the minimum proficiency level in reading.
There are other consequences to school closures. Millions of girls in some countries might not be going back at all putting them at risk of adolescent pregnancy, child marriage and violence.

Epidemics also erode health systems, disproportionately affecting those who rely most on healthcare.
We can contain epidemics before they spread through populations and over borders. We just need to prepare.
In 2018 we were able to contain outbreaks of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Nipah in Kerala, India.
Containing these events took a series of overlapping measures:
- global leadership working side by side with national governments and local health workers,
- adequate funding for research,
- and private-sector commitment.
We have a very good idea of the systems we need to put in place to stop these epidemics in their tracks. But we’re not there yet. Our safety net has too many holes that need to be mended – we must not be complacent. We need to act now to prevent a global crisis later.
Despite numerous warnings and economic calculations, the world has failed to invest in preparedness at the levels required.
Expenditures for prevention and preparedness are measured in billions of dollars, the cost of a pandemic in trillions. According to the WHO, it would take 500 years to spend as much on investing in preparedness as the world is losing due to Covid-19.
Recent research by McKinsey & Company suggests that spending approximately $85 billion to $130 billion over the next two years and approximately $20 billion to $50 billion annually after that could substantially reduce the likelihood of future pandemics. This equates to an average spend of around $5 per person annually.
With this investment, supported by global political will and private-sector involvement, we can prepare today for future outbreaks, epidemics and pandemics. The human and economic cost of ignoring the problem is too high for us not to.
This article was first published in December 2018.
We’re funding research to better understand what causes and drives infectious diseases to escalate and the solutions to control their impact.
There are currently no open funding opportunities for Infectious Disease. Learn more about the funding we provide.
Not preparing for infectious disease outbreaks costs far more than putting the systems in place to prevent them from spreading around the globe. The human and economic imperative to invest in preparedness is beyond argument.